Unlocking Software Quality: A Deep Dive into Behavior-Driven Development (BDD) and Comprehensive Testing Strategies
In today’s competitive software landscape, delivering robust, reliable, and user-centric applications is paramount. To achieve this, a synergistic approach that tightly integrates development, testing, and business objectives is crucial. One powerful technique that facilitates this integration is Behavior-Driven Development (BDD). This article provides a comprehensive exploration of BDD, its benefits, and how it aligns with various software testing methodologies to create high-quality software that meets and exceeds stakeholder expectations. We will delve into practical examples, best practices, and real-world applications to empower you to implement BDD effectively within your organization.
Demystifying Behavior-Driven Development (BDD)
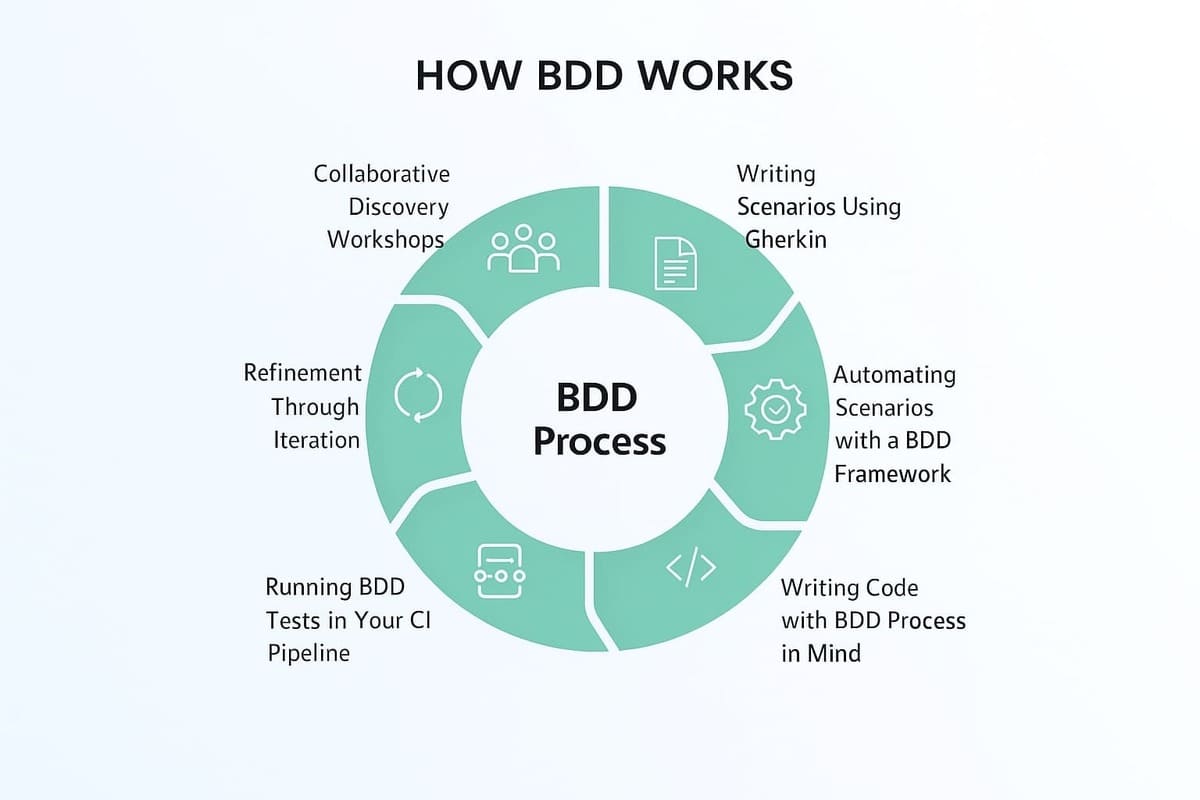
BDD is not merely a testing methodology; it’s a collaborative approach to software development that emphasizes clear communication and shared understanding between developers, testers, and business stakeholders. It’s an evolution of Test-Driven Development (TDD), focusing on behavior rather than implementation details.
Instead of writing code based on abstract technical specifications, BDD encourages defining application behavior in plain, human-readable language. These descriptions, often called “stories” or “scenarios,” articulate what the software should do from the user’s perspective, rather than how it should do it.
The core principle revolves around the “Given-When-Then” structure.
- Given: Describes the initial context or preconditions.
- When: Specifies the event or action that triggers the behavior.
- Then: Outlines the expected outcome or result.
This structure ensures that everyone involved has a clear understanding of the system’s behavior, reducing ambiguity and promoting collaboration.
The Advantages of Embracing BDD
Adopting BDD brings numerous advantages to the software development lifecycle:
Enhanced Communication and Collaboration: By using plain language scenarios, BDD fosters clear communication between technical and non-technical stakeholders. Business analysts, developers, testers, and even end-users can participate in defining and validating software behavior.
Improved Requirements Clarity: The collaborative nature of BDD forces teams to carefully consider and articulate requirements, leading to a deeper understanding of the desired functionality. Ambiguities are identified and resolved early in the process, preventing costly rework later on.
Reduced Defects and Rework: BDD helps to identify potential issues and inconsistencies early in the development cycle. This proactive approach reduces the number of defects that make it into production, resulting in significant cost savings and improved software quality.
Living Documentation: BDD scenarios serve as executable specifications that can be automatically tested. As the software evolves, these scenarios are updated to reflect the new behavior, ensuring that the documentation remains accurate and up-to-date.
Increased Test Coverage: By focusing on behavior, BDD encourages teams to develop comprehensive test suites that cover all critical aspects of the application. This leads to higher test coverage and greater confidence in the software’s reliability.
Faster Development Cycles: While the initial setup of BDD may require some investment, the long-term benefits include faster development cycles due to reduced defects, improved communication, and clearer requirements.
BDD in Action: A Practical Example
Consider an e-commerce website where customers can add items to their shopping cart. A BDD scenario for this functionality might look like this:
Feature: Add Items to Shopping Cart
Scenario: Adding a single item to the cart
Given a customer is browsing the product catalog And the customer has not added any items to their cart When the customer adds a “Red T-Shirt” to their cart Then the cart should contain one item And the cart should display the “Red T-Shirt” And the total price of the cart should be equal to the price of the “Red T-Shirt”
This simple scenario clearly describes the expected behavior of the system from the user’s perspective. Developers can use this scenario to write code that implements the desired functionality, and testers can use it to verify that the implementation is correct.
Integrating BDD with Software Testing Methodologies
BDD is not a replacement for traditional software testing methodologies; rather, it complements them. It provides a framework for defining and validating software behavior, which can then be implemented using various testing techniques. Here’s how BDD integrates with different types of software testing:
Unit Testing
Unit tests verify the functionality of individual components or units of code. In a BDD context, unit tests are often used to implement the “Given-When-Then” steps of a scenario. For example, a unit test might verify that the addItemToCart() method correctly updates the cart’s contents and total price.
Integration Testing
Integration tests verify the interaction between different components or modules of the system. In a BDD context, integration tests are used to ensure that the different parts of the application work together as expected. For example, an integration test might verify that the shopping cart module correctly interacts with the inventory management system.
System Testing
System tests verify the end-to-end functionality of the entire system. In a BDD context, system tests are used to validate that the application meets the requirements defined in the BDD scenarios. These tests often simulate real user interactions to ensure that the system behaves as expected in a production environment.
Acceptance Testing
Acceptance tests are performed by end-users or business stakeholders to verify that the software meets their needs and expectations. In a BDD context, acceptance tests are directly based on the BDD scenarios, ensuring that the software behaves as described in the requirements. This provides a clear and objective measure of whether the software is ready for release.
Other Testing Methodologies
BDD can also be integrated with other testing methodologies, such as performance testing, security testing, and usability testing. By defining clear scenarios for these types of tests, teams can ensure that the software meets all the necessary quality criteria.
Popular BDD Frameworks and Tools
Several popular BDD frameworks and tools can help you implement BDD effectively within your organization:
Cucumber: A widely used BDD framework that allows you to write scenarios in plain language using the Gherkin syntax. Cucumber supports multiple programming languages, including Java, Ruby, and JavaScript.
SpecFlow: A BDD framework for .NET that integrates seamlessly with Visual Studio. SpecFlow allows you to write scenarios in Gherkin and automatically generate test code.
JBehave: A Java-based BDD framework that supports both story-based and scenario-based testing. JBehave provides a flexible and extensible framework for defining and executing BDD tests.
Behat: A PHP-based BDD framework that allows you to write scenarios in Gherkin. Behat provides a simple and intuitive API for defining and executing BDD tests.
Robot Framework: A generic open source automation framework. It can be used for test automation and robotic process automation (RPA). Robot Framework has BDD capabilities by utilizing its keyword-driven testing approach with descriptive keywords that mirror BDD scenarios.
These frameworks provide a variety of features and tools to help you write, execute, and manage BDD tests. Choosing the right framework depends on your specific needs and technical skills.
Best Practices for Implementing BDD
To maximize the benefits of BDD, it’s essential to follow these best practices:
Start with the “Why”: Before writing any scenarios, make sure you understand the business value of the feature you’re testing. This will help you to write more meaningful and relevant scenarios.
Collaborate with Stakeholders: Involve business analysts, developers, and testers in the process of defining BDD scenarios. This will ensure that everyone has a shared understanding of the requirements and that the scenarios are accurate and complete.
Write Clear and Concise Scenarios: Use plain language and avoid technical jargon. Keep the scenarios focused on the expected behavior of the system, not the implementation details.
Use the “Given-When-Then” Structure Consistently: This will help to ensure that your scenarios are well-structured and easy to understand.
Automate Your Tests: Automate your BDD scenarios so that they can be executed repeatedly and reliably. This will help you to identify defects early in the development cycle and to ensure that the software remains working as expected.
Treat Scenarios as Living Documentation: Update your BDD scenarios as the software evolves. This will ensure that the documentation remains accurate and up-to-date.
Focus on Business Value: BDD should be centered around delivering business value. Scenarios should directly reflect user needs and contribute to a positive user experience.
Keep Scenarios Independent: Each scenario should be self-contained and not rely on the state of other scenarios. This ensures that tests are reliable and easy to debug.
Regularly Review and Refactor Scenarios: Just like code, scenarios should be regularly reviewed and refactored to improve readability, maintainability, and accuracy.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in BDD Implementation
While BDD offers numerous benefits, it’s essential to be aware of potential pitfalls:
Overly Complex Scenarios: Avoid creating scenarios that are too long or complex. Break them down into smaller, more manageable scenarios.
Focusing on Implementation Details: BDD should focus on behavior, not implementation details. Avoid including technical jargon or code snippets in your scenarios.
Lack of Collaboration: BDD requires close collaboration between stakeholders. If there is a lack of communication or teamwork, the benefits of BDD will be diminished.
Ignoring Non-Functional Requirements: BDD should not only focus on functional requirements but also on non-functional requirements such as performance, security, and usability.
Treating BDD as Just Another Testing Technique: BDD is a development philosophy, not just a testing technique. It requires a shift in mindset and a commitment to collaboration and communication.
BDD and the Future of Software Development
BDD is becoming increasingly popular as organizations recognize the benefits of improved communication, reduced defects, and faster development cycles. As software becomes more complex and user expectations continue to rise, BDD will play an even more critical role in ensuring software quality and delivering exceptional user experiences.
The evolution of BDD is also seeing greater integration with AI and machine learning. For example, AI can be used to analyze BDD scenarios and automatically generate test code, further streamlining the development process. Machine learning can also be used to identify potential risks and vulnerabilities based on BDD scenarios, enhancing the overall security of the software.
Conclusion: Embracing BDD for Software Excellence
By embracing BDD, organizations can create a more collaborative, efficient, and effective software development process. BDD helps to ensure that software meets the needs of both business stakeholders and end-users, resulting in higher quality applications that deliver exceptional value. Through clear communication, collaborative development, and comprehensive testing, BDD unlocks software excellence and helps organizations achieve their business goals. We encourage you to explore the possibilities of BDD and discover how it can transform your software development practices. By implementing BDD effectively, you can build software that is not only robust and reliable but also perfectly aligned with the needs of your users.